关于爬虫的文章,之前写过两篇:
京东那个其实也是为了写论文,虽说拿着那篇参加了个会议,但我觉得诟病比较多。
如今,为了毕业论文,又重操旧业了
这次选择的对象是苏宁易购手机评论数据
收购家乐福中国事件吸引了我的眼球
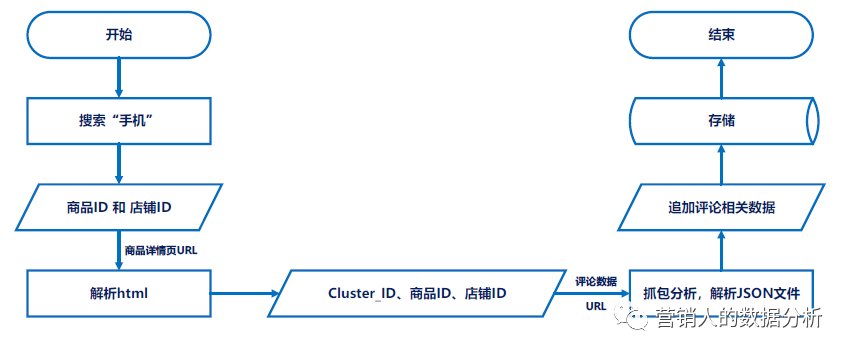
整体的逻辑也比较简单,没有很复杂的反爬技术,直接上流程图吧

提取url的共性
我觉得像我这种低端爬虫的基本思想就是所见即所得,代替人工的复制、粘贴
我们在网络上见到的东西,都会有个url与之对应
通过url给服务器发送请求
就像 https://www.baidu.com/
服务器返回相应的数据,浏览器解析这些数据,最后就是大家看到的样子

爬虫也是这个逻辑
所以写代码之前需要分析苏宁易购评论数据的url
苏宁评论数据是动态加载的,需要抓包分析
寻找url的异同点,比如不同商品、不同页面之间url的差异,哪些是变的、哪些是不变的。
一顿操作之后,发现变动的主要是三部分:
商品、店铺ID还好理解,你这个东西是什么、在哪家卖的,不能把A家商品的评论数据放到B家商品那儿
但这个 Cluster_ID 是什么
问就是不知道
但还是要清楚这玩意儿可以从哪儿得到,不然评论数据的url也不知道呀
有幸结识了位美团的前端大佬,在大佬的帮助下,找到了Cluster_ID
结论是,在商品详情页的源代码中有这么个东西
所以在最终确定评论数据的URL之前,需要通过解析商品详情页的数据,获取 Cluster_ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
def get_clusterId(product_id,ua,shop_id="0000000000"):
'''
解析商品详情页url 得到clusterId
'''
url = "https://product.suning.com/{}/{}.html".format(shop_id,product_id)
header = {"Referer":"https://search.suning.com/%E6%89%8B%E6%9C%BA/#second-filter","User-Agent": ua}
response = requests.get(url, headers=header)
html = response.text
soup = bs(html,"html.parser")
t = soup.select("head script")[0]
tstr = t.get_text()
cluster_id = re.search(r"clusterId\":\"(\d*).*?\"",tstr).group(1) # string
return cluster_id
|
shop_id=0000000000 表示店铺是苏宁自营
正如流程图中所示,通过商品、店铺ID,确定商品详情页的url,从服务器返回的数据中找到 Cluster_ID
其实到这,就已经结束了
后续的操作就是获取并解析json文件
json文件
根据url请求服务器,让其返回评论数据的json文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
def again_content(cluster_id,product_id,page,ua,shopid="0000000000"):
product_id_0 = "0"*(18-len(str(product_id))) + str(product_id)
url = "https://review.suning.com/ajax/cluster_review_lists/cluster-{}-{}-{}-again-{}-default-10-----reviewList.htm?callback=reviewList".format(cluster_id,product_id_0,shopid,page)
header = {"User-Agent": ua,
"Referer":"https://product.suning.com/{}/{}.html".format(shopid,product_id),
"Host": "review.suning.com",
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"Accept-Language": "zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,zh-TW;q=0.8,en;q=0.7"}
response = requests.get(url, headers=header)
html = response.text
text = json.loads(html.lstrip("reviewList(").rstrip(")") )
reviews = text["commodityReviews"]
print(text["returnMsg"],product_id,page)
return reviews
|
根据json文件找到想要的数据,根据key-value的对应形式,慢慢获取就可以了,如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
add_reviewID = reviews["againReview"]["againId"]
reviewId = reviews["commodityReviewId"] # 之后要利用这个匹配 useful_vote
first_review = reviews["content"]
first_review_pt = reviews["publishTime"]
add_review = reviews["againReview"]["againContent"]
add_review_pt = reviews["againReview"]["publishTime"]
diff_first_add_pt = reviews["againReview"]["publishTimeStr"]
qualityStar = reviews["qualityStar"]
first_pic = reviews["imgCnt"]
|
最后保存相关数据即可
其他细节
循环次数
因为我是 FOR 循环的形式获取评论数据的,并且有些商品的追评数据比较少。为了避免无效的循环,所以我还额外通过追评总数计算了页面数,以决定循环次数。最多展示50页
反反爬
这里面学问比较多,对效率要求不高的话,可以设置停留时间,休息一会儿再请求服务器
模拟随机的UserAgent,就像是换个浏览器
这个时候就要安利下fake_useragent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import time
import numpy as np
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
# 随机休息3-10秒
time.sleep(np.random.randint(3,10))
# useragent
ua = UserAgent()
ua.random
|
其实,最好的方法是随机更换IP地址
增强稳健性
为了保证代码的正常运行,预判会报错的地方,采取相应的方式
爬虫主要是以放服务器拒绝请求
我的方式比较粗暴,歇息时间长一点继续工作
1
2
3
4
5
|
try:
clusterId = get_clusterId(product_id,ua.random)
except:
time.sleep(np.random.randint(5,15))
continue
|

 胡子叔叔的小站
胡子叔叔的小站